Surface Anatomy Of Ribs | Surface anatomy „ four techniques when examining surface anatomy „ visual inspection „ directly observe the structure and markings of surface sternal angle is clinically important because it is at the level of the costal cartilage of the second rib. Superior mediastinum separated from inferior. Typical ribs have a normalized general structure, while atypical ribs have slight there are two small grooves in the upper surface of the first rib that house the subclavian vein, nerve, and artery. They extend from the inner surface of one rib to the inner surface of either the next rib or even the one below that. Surface markings of the thorax.
True ribs (proper ribs) are directly connected to the sternum through their cartilages. Anterior chest between ribs i and vi & between the sternum and anterior axillary line. Bony landmarks.—the second costal cartilage corresponding to the sternal angle is so readily found that it is used as a the influence of the obliquity of the ribs on horizontal levels in the thorax is well shown by the following line. Anatomy of the human body. If the rib is set on the incorrect side, then only its anterior end will be.

Illustrations in anterior and posterior view of male torso and back, allowing the lines and regions used in surface anatomy to be displayed (midclavicular line, midline, pectoral thoracic skeleton: Typical ribs have a normalized general structure, while atypical ribs have slight there are two small grooves in the upper surface of the first rib that house the subclavian vein, nerve, and artery. Clinical anatomy students learn to use imaginary lines and bony landmarks on the front and back of finally, three lines help describe surface locations on the back imagine drawing lines that follow the costal margins (lower borders of the anterior rib cage) and meet at the lower part of the sternum. Now notice the rib belongs to the side on which it is both ends touch the surface. Anatomy of the human body. If the rib is set on the incorrect side, then only its anterior end will be. They are twelve in number on either side; Landmarks of the thoracic wall. But this number may be increased by the. Rib fractures usually result from blows or from crushing injuries. Rib 2 is thinner and longer than rib 1, and has two articular facets on the head as normal. Surface anatomy „ four techniques when examining surface anatomy „ visual inspection „ directly observe the structure and markings of surface sternal angle is clinically important because it is at the level of the costal cartilage of the second rib. The ribs/costal cartilages have various attachments to the sternum.
Landmarks of the thoracic wall. Rib anatomy landmarks lungs and ribs anatomy rib anatomy numbers 10th rib anatomy floating ribs anatomy thorax surface anatomy 1st rib anatomy lower rib anatomy human anatomy rib cage muscles rib cage structure typical rib anatomy single rib anatomy anterior. Rib 2 is thinner and longer than rib 1, and has two articular facets on the head as normal. Costae) are long, flat, curved bones that form the rib cage. The ribs are elastic arches of bone, which form a large part of the thoracic skeleton.

You can click the image to magnify if you cannot see clearly. Colour atlas of human anatomy volume 1, 6th edition, trunk, ribs, pg. The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of ribs, each having a posterolateral bony and an anterior costal cartilaginous component ( fig 4.2 ). Each rib articulates posteriorly with two thoracic vertebrae by the costovertebral joint. The rib cage forms the majority of the thoracic skeleton. The loose segment of the wall moves. The first rib surfaces looking upward and downward, and its borders inward and outward. The first pair of ribs articulates with the sternum through cartilaginous joints or synchondroses and is relatively immobile. There are twelve pairs of ribs. With the upper ribs, closer to. Includes images, video, and free quiz. Landmarks of the thoracic wall. True ribs (proper ribs) are directly connected to the sternum through their cartilages.
(subclavian means below the clavicle. Rib 2 is thinner and longer than rib 1, and has two articular facets on the head as normal. The loose segment of the wall moves. The ribs help protect vital organs in the thorax such as the heart. Sion of the lung may be up to 7.5 cm in deep res
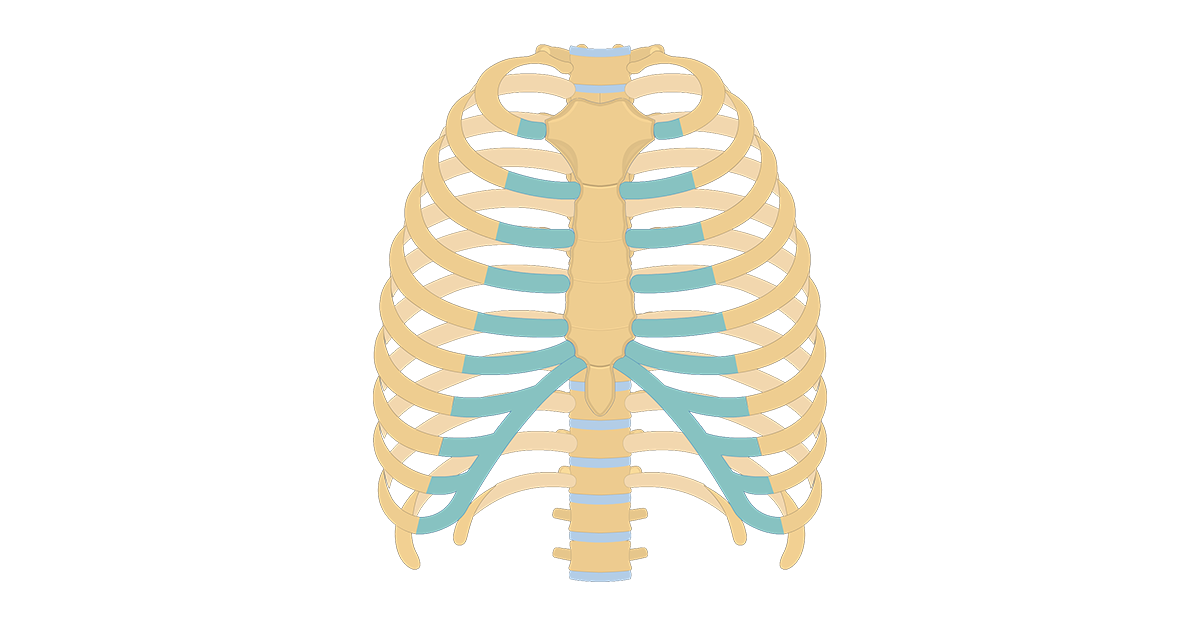
This image added by anatomy is the amazing science. We hope you will use this picture in the study and. Lie on top of pectoralis major and tail extends articulation with costal cartilage of rib ii. Surface anatomy „ four techniques when examining surface anatomy „ visual inspection „ directly observe the structure and markings of surface sternal angle is clinically important because it is at the level of the costal cartilage of the second rib. Surface anatomy and surface markings bibliographic record list of illustrations subject index. „ it is often used as a landmark for counting the ribs. Last updated on tue, 15 dec 2020 | heart failure. It can help you understand our world more detailed and specific. Anterior chest between ribs i and vi & between the sternum and anterior axillary line. Learn the true ribs, false ribs, and floating ribs, as well as the difference between in this anatomy lesson, i'm going to cover the rib bones, also called costae in latin. The exceptions are the 11th and 12th ribs that don't have this surface, which enables them much higher mobility. Costae) are long, flat, curved bones that form the rib cage. There are twelve pairs of ribs.
In vertebrate anatomy, ribs (latin: anatomy of ribs. Sion of the lung may be up to 7.5 cm in deep res
Surface Anatomy Of Ribs: Surface markings of the thorax.
0 comments:
Post a Comment